Scientific basis of soy sauce production technology
Use of enzyme preparations in pure form or in semi-pure or crude form such as: termamyl, speczymes (containing amyloglucosidase), protamex (containing bacterial protease), novozym, flavourzyme ...) and enzymes such as protease, Pepsin, trysin, amylase, lipase ... hydrophilic protein in raw materials into soy sauce.
Protein hydrolysis is the basis of soy sauce processing technology:
The essence of protein hydrolysis is peptide linkage hydrolysis. Because peptide bonds are a strong link, hydrolysis occurs under catalytic conditions. Chemical catalysts are acids or alkalis and agents. Bio-chemical catalysis is a group of proteolytic enzymes called proteases.
Soy sauce production process
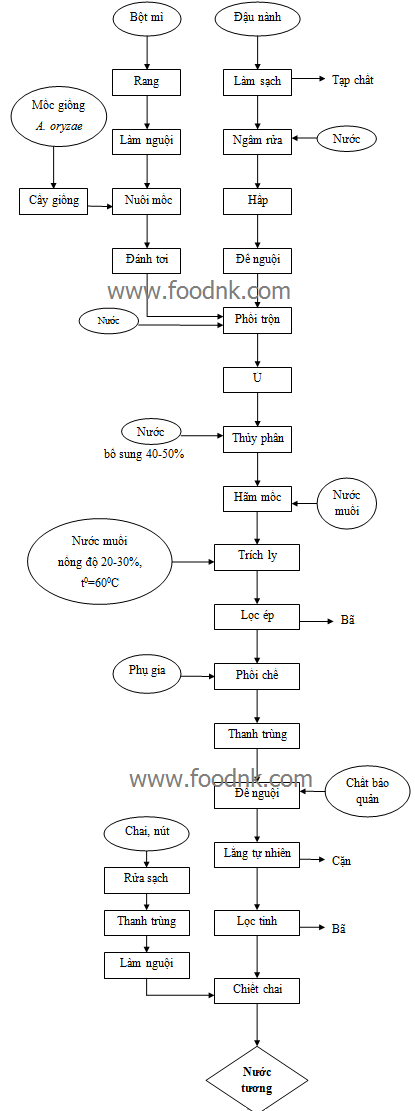
Explain the process
1. Clean
Removing foreign objects, broken particles in the pile of particles or impurities clinging to the surface of the shell. The following processes are easy to do (helping to wash faster, to filter faster, avoid contamination during incubation), increase the quality of raw materials.
Method of implementation: can be done by different methods such as for soybean through the classification system by photovoltaic cells, multi-layer screen sieve system ...
2. Soak
Wash the wrong purpose of cleaning the impurities left after the cleaning process and soften the beans to save time and fuel during the steaming process.
During soaking, soy can lose some soluble nutrients such as vitamins and minerals.
Perform
The process consists of two stages: soaking and rinsing. First, the material is fed to the pickling basin and then conveyed to the irrigation system. Soaking makes the water soak the material, making the dirt soft, peeling off. Flushing is the use of the flow of water to remove dirt remaining on the material after soaking. Usually use water spray (p = 2-3at) or shower to flush.
3 Steam
Misbehaving process exploits nutrients in soybeans, denatured proteins in soybeans make microorganisms easier to use, making the process easier and time saving. It also helps to thoroughly remove the foreign microorganisms to avoid contamination during the tempering process.
Changes in the steaming process
- Physics: changes in starch and protein grain structure, softer materials.
- Chemistry: ripening starches, making proteins preliminarily denominated into substances that microorganisms can use.
- Biology: This process kills the microorganisms that cling to the surface of the material to make the mold develop smoothly.
Method of implementation and specifications
+ Raw materials are just soaked with just how long it takes to have the right amount of water and the raw material is sufficiently softened.
+ For starch raw materials, the steaming time should also be reasonable
With the above requirements, steaming at a pressure of 0.7-0.9 kg / cm2, steaming about 1-1.5 hours is appropriate. When the grain turns brown the steaming process can stop.
4. Cool
Soaking soybeans after steaming to avoid killing mold and dissolve wheat flour when mixed makes it difficult to ferment fermentation on the surface of the grain.
Transformations
- Physical: Material left out, material block temperature decreased.
- Physics: there is evaporation
Method of implementation and specifications: The steamed material is spread on a wooden floor with a cooling fan of 30-350C (summer) and about 400C (winter). When cooling should be placed in a clean environment to avoid contamination for subsequent mixing.
5. The mold raising process
The flour material is roasted, then spread evenly on the flat floor so that the temperature of the material block drops, the process is supported by the blower system.
• Transplant
Mold is the basis for the production of fermented soy sauce, mold quality directly affects the quality of the product and the efficiency of using raw materials.
Methods of implementation
When putting in the seed should be mixed with some flour for all, then use this material sprinkled on the material to propagate. When sprinkler should be mixed thoroughly to have mold evenly across the block of material and mold development evenly also cause the material block temperature increase consistently.
• moldy
Facilitate the growth of the mold on the culture medium, forming the necessary enzymes (especially protease and amylase) with high activity, capable of hydrolyzing protein and starch higher.
Method of implementation and specifications
Wheat flour mixed will be the starch source that mold used as a food source to grow and flourish. The strong development of seed markers will overwhelm the other types of landforms that will penetrate and develop, resulting in higher levels of hydrolysis.
During mold growth, the temperature is directly related to the reproduction of the mold. The temperature of the material will increase with the development of the mold and may reach up to 450C if left unused. So we have to mold mold to regulate the temperature and humidity in the mold material to promote the growth of the company. Production practices for many years have shown that molding at room temperature of 28-300C and moisture content of 27-37% will give protease activity and






